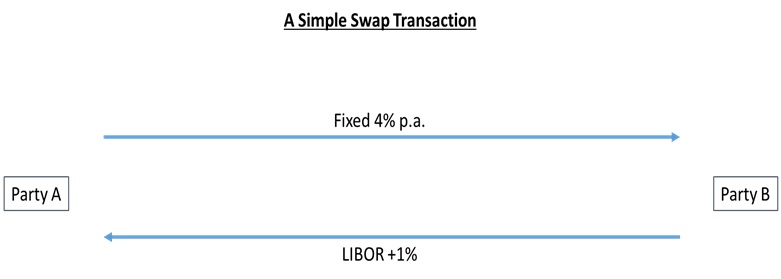
This is a simple Derivative Swap Transaction, wherein Party A agrees to pay Pary B a fixed return periodically,
while Party B agrees to pay Party A, a floating rate (LIBOR +1%). The reasons can be many for each of these parties to enter into such a transaction.
Some of the basic reasons for these parties to enter into such a SWAP transaction:
- Balance sheet hedging
- Party A believes floating rate will go higher than the agreed fixed rate; Party B believes floating rate will go lower than the fixed rate here
- They may have opposite positions that they want to hedge using this SWAP transaction
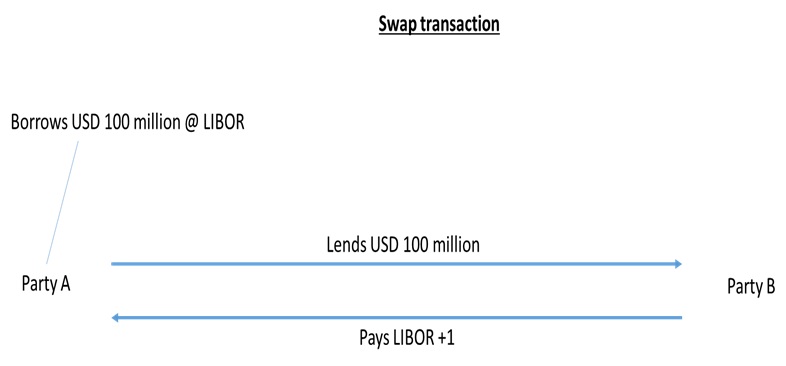
Example 2: