Of late, mutual funds have become a hot favorite of millions of people all over. The driving force of mutual funds is the ‘safety of the principal’ guaranteed, plus the added advantage of capital appreciation together with income earned from dividends.
Mutual funds scores over bank Fixed Deposits or other insurance products as mutual fund allows an investor to get into the investment game (equities, etc) with very little investment.
An investor can own blue chip stocks or high value stocks like Reliance, ITC, TISCO, HDFC Bank, etc through investment in mutual funds. Thus, mutual fund acts as a gateway to enter into high-ticket stocks even with very less investment.
In simple words, a mutual fund collects the savings from millions of individuals (small, medium and large investors) and invests the money so collected into Securities, Bonds, etc of either private, public companies or government instruments. Some mutual funds also invests in Derivative instruments, depending on what type of fund is it. Once needs to invest in the type of fund that suits my risk taking ability.
The logic of the mutual fund is simple: if one person has INR 1000 to invest, he has very little option available with him and accordingly it will fetch him limited returns. But if INR 1000 are collected from lakhs of individuals, we have with us a huge corpus of funds. This large corpus of funds when invested, many investment opportunities are available and returns are handsome, even risk can be mitigated as investment in mutual fund will ensure that investments are made in diversified manner – taking into account different instruments or different sectors.
Thus, every investor, whether big or small, will have a stake in the fund and can enjoy the wide portfolio of the investment held by the fund.
Mutual fund has emerged as a popular vehicle for creation of wealth due to lower costs, higher returns and diversified risks.
Definition:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1993 defines a mutual fund as a “fund established in the form of a trust by a sponsor, to raise monies by the trustees through the sale of units to the public, under one or more schemes, for investing in securities in accordance with these regulations. “
Origin:
The origin of the concept of mutual fund dates back to ages in human history. But the real credit of introducing the modern concept of mutual fund goes to the Foreign and Colonial Government Trust of London established in 1868. Thereafter, a large number of close-ended mutual funds were formed in the USA in 1930s followed by many countries in Europe, the Far East and Latin America. In most of the countries, both open-ended and close-ended types were popular. In India, it gained momentum only in 1980, though it began in the year 1964 with the Unit Trust of India launching its first fund, the Unit Scheme 1964.
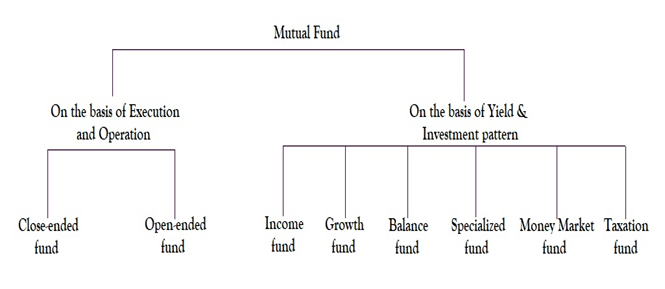
Diagram: Mutual Fund classification